What Are Environmental Accreditations: Purpose and Importance
Environmental Certifications are official recognitions granted to organizations, products, or services that meet specific environmental performance standards. They serve as proof of commitment to sustainability, responsible resource use, and environmental protection. These certifications are awarded by recognized bodies after a thorough evaluation process, often involving on site audits, data analysis, and compliance checks.
For businesses, obtaining an environmental accreditation is more than a badge it is a strategic tool. It enhances brand credibility, improves market positioning, and ensures compliance with regulations. For consumers and stakeholders, Certifications offer reassurance that claims about environmental responsibility are genuine and verified.
Environmental accreditations also play a critical role in achieving ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) goals, contributing to carbon reduction targets, and helping companies stand out in competitive markets. With the global shift toward greener economies, these certifications have become a business necessity rather than an optional extra.
Essential Environmental Management Certifications: Spotlight on ISO 14001
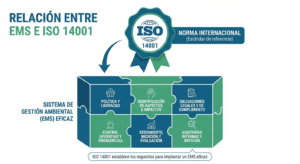
Among the many environmental Certifications, ISO 14001 stands out as one of the most recognized international standards for Environmental Management Systems (EMS). Published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), it provides a framework for organizations to manage environmental responsibilities systematically.
Key benefits of ISO 14001 include:
- Regulatory compliance: Ensures alignment with environmental laws and regulations.
- Operational efficiency: Encourages better use of resources and waste reduction.
- Risk management: Identifies and mitigates environmental risks before they escalate.
- Market advantage: Enhances reputation and attracts environmentally conscious clients.
Implementing ISO 14001 involves establishing policies, setting measurable environmental objectives, training staff, and conducting internal audits. Certification is granted after an independent audit confirms compliance. This accreditation is applicable to organizations of all sizes and industries, from manufacturing to services.
Globally Recognized Environmental Certifications and What They Verify
While ISO 14001 focuses on environmental management systems, other certifications target specific aspects of sustainability:
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) – Recognizes sustainable building design, energy efficiency, water conservation, and use of sustainable materials.
- BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) – Evaluates building performance, energy use, water management, materials, health, and innovation.
- ENERGY STAR – Certifies energy-efficient appliances, electronics, and buildings.
- FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) – Guarantees responsible forest management and sustainable timber products.
- Rainforest Alliance Certified – Ensures agricultural products meet environmental, social, and economic sustainability criteria.
- FairTrade – Promotes fair wages, ethical sourcing, and sustainable production.
- Green Seal – Recognizes eco-friendly products and services meeting strict performance and sustainability standards.
- B Corp Certification – Assesses a company’s overall social and environmental performance.
These accreditations collectively cover diverse sectors, from construction and agriculture to manufacturing and retail, making them essential tools in the sustainability ecosystem.
Classification and Key Features of Major Environmental Certifications
- Environmental Management Certifications: Certifications that recognize the implementation of organized systems to manage environmental impacts, improve ecological performance, and comply with environmental regulations
- Energy and Climate Certifications: Certifications that assess and promote energy efficiency, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, and contribution to climate change mitigation
- Sustainable Building and Construction Certifications: Certifications focused on the construction and design of sustainable buildings, considering energy efficiency, resource use, occupant health, and life cycle sustainability.
- Product and Material Certifications: Certifications that verify that products, materials, or processes meet environmental and sustainability standards, minimizing ecological impact and promoting responsible consumption.
- Food and Agriculture Certifications: Certifications that ensure sustainable, healthy, fair, and environmentally and socially responsible agricultural and food production practices.
- Circular Economy and Waste Certifications:Certifications that recognize strategies for prevention, reuse, recycling, and waste reduction, promoting a sustainable material life-cycle.
- Corporate and Comprehensive Sustainability Certifications: Certifications that comprehensively assess a company’s environmental, social, and ethical performance, promoting responsible corporate practices.
This classification allows organizations to identify which certification aligns best with their operations, goals, and industry-specific needs.
How to Choose the Right Certifications for Your Organization
Selecting the right environmental accreditation depends on several factors:
- Industry sector: Construction may benefit from LEED or BREEAM, while agriculture aligns with Rainforest Alliance or FairTrade.
- Geographic market: Some accreditations are more recognized in certain regions (e.g., BREEAM in Europe, LEED in the US).
- Environmental priorities: Organizations focused on carbon reduction might prioritize ISO 14064, while those aiming for holistic sustainability could pursue B Corp.
- Customer expectations: Understanding stakeholder preferences ensures the certification adds tangible value.
An internal sustainability audit is recommended before choosing, ensuring the selected accreditation supports both environmental and business objectives.
Strategies for Integrating Certifications into Your Environmental Strategy
Once obtained, an accreditation should not be treated as a static achievement. Instead, it must be integrated into business strategy:
- Include certification requirements in procurement policies.
- Train staff on maintaining compliance.
- Use certifications in marketing campaigns to highlight credibility.
- Monitor and report progress to stakeholders annually.
Continuous improvement is key. Environmental standards evolve, and maintaining certification demonstrates long-term commitment to sustainability.
Real Impact and Challenges: From Credibility to Greenwashing
Environmental accreditations add legitimacy, but they also face challenges:
- Credibility risks: Weak standards or poor enforcement can erode trust.
- Costs: Certification processes can be resource-intensive, especially for small businesses.
- Greenwashing: Misusing certification logos or making unverified claims can damage reputation.
To counter these risks, organizations should be transparent, choose reputable certifying bodies, and communicate results honestly.
Global and Local Perspectives: Examples from Different Regions
- Europe: Strong regulatory frameworks make accreditations like BREEAM and ISO 14001 highly valuable.
- North America: LEED, ENERGY STAR, and WELL dominate due to market demand and governmental incentives.
- Latin America: EDGE is gaining traction due to cost-effectiveness, alongside Rainforest Alliance in agriculture.
- Asia-Pacific: Focus on ISO 14001 and region-specific green building codes.
Understanding regional contexts helps organizations choose the most impactful and recognizable certifications.