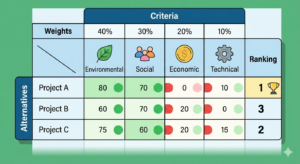
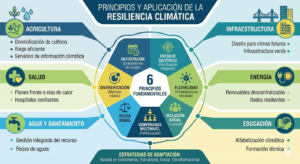
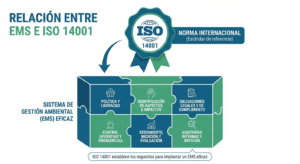
Environmental challenges are transforming how organizations operate worldwide. From international agencies to private companies, adopting environmental guidelines is no longer optional it is essential for transparency, compliance, and long term sustainability.
This guide brings together the most relevant frameworks, including green procurement guidelines and SECR reporting guidance, along with practical examples and future trends.
What Are Environmental Guidelines?
Environmental guidelines are frameworks that provide organizations with clear directions for managing environmental impacts responsibly. They may be regulatory or voluntary, and they cover reporting, procurement, operations, and management practices.
Key Objectives and Benefits
- Provide consistent direction for environmental management.
- Ensure regulatory compliance and credibility.
- Facilitate sustainable decisionmaking in operations and supply chains.
- Build trust with regulators, investors, and stakeholders.
Regulatory vs. Voluntary Guidelines
- Regulatory guidelines: Mandatory frameworks such as the UK’s SECR reporting guidance.
- Voluntary guidelines: Global initiatives such as the GRI Standards or CDP disclosure programs, used to demonstrate sustainability leadership.
Difference Between Environmental Guidelines, Standards, and Certifications
- Environmental Guidelines: Provide frameworks and recommendations (e.g., reporting or procurement guidelines).
- Environmental Standards: Define measurable, auditable requirements (e.g., ISO 14001).
- Environmental Certifications: Confirm that an organization meets guidelines or standards, validated by third parties (e.g., LEED, BREEAM).
| Aspect | Environmental Guidelines | Environmental Standards | Environmental Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recommendations or best practices aimed at protecting the environment. | Specific technical requirements to ensure environmental performance. | Formal recognition that an organization, product, or service meets certain environmental standards. |
| Mandatory? | Generally voluntary. | Mandatory if adopted by law, regulation, or contractual agreement. | Voluntary, but provides competitive and reputational value. |
| Main Purpose | Guide decision-making and sustainable practices. | Ensure consistency and environmental quality in processes, products, or services. | Validate and certify environmental compliance to third parties and consumers. |
| Examples | UN Climate Change Guidelines, WHO Environmental Health Guidelines. | ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), national air and water emission limits. | LEED (green building), Energy Star, FSC (sustainable forestry). |
| Audit / Verification | No formal audit required; often self-assessed. | Typically verified through inspections or technical reports. | Requires external audit by certified bodies. |
| Impact | Raises awareness and improves internal practices; indirect sustainability benefits. | Ensures legal compliance and reduces environmental risks. | Builds credibility, recognition, and market advantage. |
| Update Frequency | Flexible; updated based on new research or recommendations. | Rigid; updated formally by regulatory bodies. | Depends on periodic recertification. |
Types of Environmental Guidelines: A Complete Overview
Environmental Reporting Guidelines
These focus on disclosing emissions, waste management, energy use, and sustainability performance.
Green Procurement Guidelines
Green procurement guidelines encourage sustainable purchasing practices, such as:
- Prioritizing recycled or renewable materials.
- Reducing energy consumption in supply chains.
- Selecting suppliers with sustainability certifications.
SECR Reporting Guidance
The Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) guidance requires large UK companies to disclose energy consumption, emissions, and efficiency measures in annual reports.
Operational/Management Guidelines
Cover day to day activities such as waste handling, facility energy efficiency, and safe use of chemicals.
Environmental Management Standards
Standards such as ISO 14001 establish measurable requirements for systematic environmental management.
Examples of Environmental Guidelines: EPA and SECR
EPA Guidelines for Radon
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) publishes guidelines for specific risks, such as radon mitigation, providing step by step procedures for schools, businesses, and households.
SECR Reporting Guidance
The UK’s SECR framework is one of the clearest examples of mandatory environmental guidelines.
Steps to Ensure Compliance
- Identify if your business qualifies under SECR rules.
- Collect accurate data on energy use and emissions.
- Document efficiency measures implemented.
- Integrate disclosures into annual reporting.
Comparing the Main Frameworks
Overlaps and Differences
- Reporting guidelines: focus on disclosure.
- Procurement guidelines: purchasing and supply chain sustainability.
- SECR: mandatory energy and carbon reporting in the UK.
Which Guidelines Apply to Your Organization?
- Public institutions → operational and reporting guidelines.
- Corporations → procurement + reporting guidelines.
- UK businesses → SECR reporting is mandatory.
How to Implement Environmental Guidelines Effectively
Best Practices
- Conduct a materiality assessment to identify priority impacts.
- Adopt recognized frameworks (GRI, SECR, green procurement).
- Include sustainability clauses in supplier contracts.
- Use digital tools for accurate environmental data collection.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Treating guidelines as a one-off compliance exercise.
- Ignoring supply chain impacts.
- Applying inconsistent metrics.
- Failing to link guidelines with corporate strategy.
Future Trends in Environmental Guidelines
Digital Tools and ESG Integration
AI, blockchain, and cloud based platforms are revolutionizing how companies implement and monitor guidelines. Increasingly, environmental guidelines are expected to align seamlessly with ESG frameworks.
Supply Chain Transparency
Over 70% of emissions in many industries occur in supply chains. Future environmental guidelines will demand full traceability in sourcing, packaging, and logistics, with green procurement guidelines at the center.
FAQs on Environmental Guidelines
What are environmental guidelines?
Frameworks that direct organizations in managing and disclosing environmental practices.
What are green procurement guidelines?
Rules that require organizations to consider environmental impacts when purchasing products or services.
What is SECR reporting guidance?
A UK regulatory framework requiring disclosure of energy consumption, emissions, and efficiency measures.
What is the difference between guidelines, standards, and certifications?
Guidelines orient, standards define requirements, and certifications verify compliance.
Why are environmental guidelines important?
They improve sustainability performance, ensure compliance, and build trust with stakeholders.