What Are Environmental Standards?
Environmental standards are sets of rules, guidelines, or benchmarks designed to protect the environment and promote sustainable practices. They define acceptable levels of emissions, waste management, energy efficiency, and resource use across industries. Governments, international organizations, and private entities use these standards to regulate environmental performance and encourage continuous improvement.
These standards serve as both a regulatory tool (for compliance) and a business strategy (for competitiveness, reputation, and access to international markets). They play a critical role in aligning companies with global sustainability goals such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Are Environmental Standards and Environmental Certifications the Same?
While often used interchangeably, environmental standards and environmental certifications are not the same:
- Environmental Standards → Guidelines or requirements that define how organizations should operate to minimize environmental impact (e.g., ISO 14001, LEED framework, EU directives).
- Environmental Certifications → Formal recognition granted by an accredited third-party auditor once an organization demonstrates compliance with a specific environmental standard.
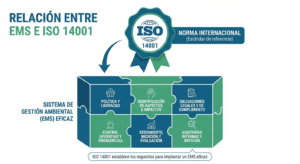
👉 Example: ISO 14001 is the standard, while an accredited certificate confirming compliance is the certification.
This distinction is crucial for businesses because standards provide the framework, and certifications deliver the proof of compliance that customers, regulators, and investors demand.
Main Types of Environmental Standards
International Environmental Standards
- ISO 14001 – Environmental Management Systems.
- ISO 50001 – Energy Management Systems.
- ISO 14064 – Greenhouse Gas Emissions Management.
National and Regional Standards
- European Union Directives (emissions, waste, energy efficiency).
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations.
- National sustainability laws and frameworks worldwide.
Industry Specific Standards
- LEED, BREEAM, Green Star, HQE – Building and construction.
- FSC, MSC, ASC – Forestry, fishing, and aquaculture.
- EPEAT, Energy Star – Electronics and energy performance.
Certifiable vs Non Certifiable Environmental Standards
Examples of Certifiable Standards
These allow organizations to obtain an official certificate after external audit:
- General / Multisectoral: ISO 14001, EMAS (EU), ISO 50001.
- Construction: LEED, BREEAM, Green Star, HQE, Passive House, EDGE.
- Energy / Industry: Energy Star, ISO 14064.
- Agriculture / Forestry / Fisheries: FSC, MSC, ASC, Rainforest Alliance, GLOBALG.A.P., Organic (EU/USDA).
- Electronics / Products: EPEAT.
Examples of Non-Certifiable Standards
These provide guidelines and frameworks but do not grant direct certification:
- General / Multisectoral: ISO 14004, ISO 26000, UN SDGs, GRI Standards.
- Energy / Industry: ISO 14067 (carbon footprint), ISO 14046 (water footprint), ISO 14040/44 (life cycle analysis).
- Regulatory frameworks: EU and national environmental laws, emission limits, hazardous waste regulations.
👉 Businesses often use non certifiable standards as a foundation, then pursue certifiable ones to demonstrate verified compliance.
Why Environmental Standards Matter for Businesses and Governments
Compliance and Legal Obligations
Meeting standards ensures organizations avoid fines, legal actions, and reputational risks. In many regions, compliance with certain environmental standards is mandatory.
Competitive and Reputational Advantages
Companies certified under recognized standards gain a strong marketing edge, build trust with eco-conscious consumers, and often qualify for government incentives and international contracts.
Challenges in Implementing Environmental Standards
- Initial cost of certification and audits.
- Need for specialized staff training.
- Complex documentation and continuous monitoring.
- Balancing short-term costs with long-term sustainability gains.
The Future of Environmental Standards and Sustainability Goals
Environmental standards will continue evolving to address climate change, circular economy, carbon neutrality, and ESG reporting. Businesses that adopt these frameworks early will be better positioned to compete in a sustainability-driven global economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are environmental standards and why are they important?
They are rules and benchmarks that guide organizations toward sustainability and legal compliance.
What is the difference between ISO 14001 and other standards?
ISO 14001 is a management system standard, while others may focus on specific sectors like construction (LEED) or forestry (FSC).
Who defines environmental standards?
They are set by international organizations (ISO, UN), governments, and independent bodies.
How do environmental standards impact businesses?
They reduce risks, open market opportunities, and boost reputation while ensuring compliance.