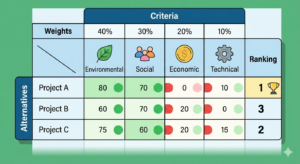
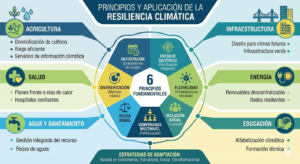
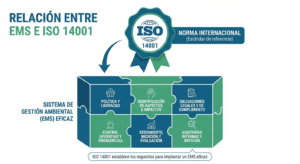
Environmental planning has become a core discipline for governments, companies and communities seeking to balance development with ecological protection. Rather than reacting to environmental damage after it occurs, environmental planning provides a structured, science based framework to anticipate impacts, guide land use, design sustainable policies, and build resilient territories.
¿What Is Environmental Planning?
Environmental planning is the process of integrating environmental knowledge into decision making to ensure that land development, infrastructure, economic activity and urban growth are compatible with long term ecological sustainability.
It assesses how human systems interact with natural systems and builds strategies to avoid degradation, prevent risk, and promote responsible use of natural resources
A Practical Definition
- Environmental planning provides a roadmap that determines:
- What environmental challenges exist
- What sustainability goals must be achieved
- Which actions, policies and programs are required
- How progress and impact will be monitored
- In short, it connects environmental science, public policy, territorial management and urban planning under one coordinated framework.
Environmental Planning vs. Environmental Management
While related, they are not identical:
Environmental management → operational, focused on day to day implementation
Environmental planning → broader, strategic, future oriented
Main Goals of Environmental Planning
Protecting Natural Systems
- Environmental planning works to safeguard:
- ecological corridors
- wetlands and watersheds
- vulnerable habitats
- biodiversity hotspots
Encouraging Sustainable Development
It ensures that the built environment evolves without exhausting the ecological systems that support it.
Reducing Environmental Risks
By identifying hazard zones such as flood areas, unstable slopes or areas prone to environmental degradation planning reduces vulnerability and protects communities.
The Environmental Planning Process
Baseline Assessment
A full environmental diagnosis that includes:
- water, air and soil conditions
- land use patterns
- environmental pressures
- climate risks
- regulatory constraints
Setting Objectives & Sustainability Targets
Clear, measurable goals such as:
- emission reduction
- habitat conservation
- improved water quality
- circular resource use
Designing Policies, Programs & Strategies
Based on the diagnosis, authorities or organizations define programs including:
- waste management improvement
- green infrastructure
- renewable energy integration
- ecological restoration
Implementation & Stakeholder Participation
At this stage budgets, responsibilities, timelines and community engagement strategies are established.
Monitoring & Continuous Improvemen
Evaluation indicators assess performance and guide new decisions.
Key Tools and Instruments in Environmental Planning
Strategic Instruments
- land use plans
- environmental zoning
- regional planning frameworks
- protected area strategies
Regulatory Instruments
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA)
- environmental permits and licenses
- emission standards & compliance rules
Corporate Instruments
- Environmental Management Systems (ISO 14001)
- sustainability action plans
- environmental audits
- carbon and resource efficiency programs
Environmental Planning in Urban and Regional Contexts
- Urban Mobility & Infrastructure: Sustainable transportation, road networks, green corridors and transit oriented development.
- Water, Air and Noise Management: Policies to reduce pollution and manage environmental quality in densely populated cities.
- Risk Prevention and Climate Adaptation: Focus areas include:
- coastal erosion
- climate driven flooding
- urban heat islands
- emergency management planning
International Approaches to Environmental Planning
United States
Guided by NEPA, CEQA and extensive evaluation procedures (EIS, EA).
European Union
Strong focus on circular economy, biodiversity and long term zero waste targets.
Latin America
Increasing integration between land use planning and environmental policy.
Asia Pacific
Countries like the Philippines and Australia have robust legal systems that align urban growth with environmental performance.
Where Environmental Planning Is Applied
Businesses & Industry
- emissions reduction
- environmental risk management
- energy efficient production
Local Governments
- zoning and territorial planning
- green public infrastructure
- ecosystem protection policies
Major Infrastructure Projects
Highways, airports, mining projects, ports and hydroelectric plants must integrate environmental planning to minimize irreversible impacts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is environmental planning important?
Because it prevents environmental damage before it occurs and ensures sustainable economic and urban development.
Who performs environmental planning?
Urban planners, environmental scientists, policymakers, engineers and consulting firms.
Is environmental planning mandatory?
In most countries, yes especially for major infrastructure projects or land use changes.