What Is the Area of Influence?
The Area of Influence refers to the geographical space where a project, activity, or development may generate environmental, social, or economic effects, either directly or indirectly. This concept is a core element of Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA), as it defines the spatial boundaries within which impacts must be identified, analyzed, and managed.
From a technical perspective, the Area of Influence connects project actions with environmental components physical, biological, and socio-economic ensuring that the assessment reflects real world conditions and potential interactions.
Why the Area of Influence Is Critical in Environmental Impact Assessments
A properly defined Area of Influence is essential because it:
- Establishes the spatial scope of impact identification.
- Determines which ecosystems, communities, and resources may be affected.
- Supports the design of mitigation and management measures.
- Helps identify environmentally or socially sensitive areas.
- Strengthens the technical validity of the EIA.
An incorrect or poorly justified Area of Influence can lead to underestimated impacts, regulatory issues, or ineffective environmental management decisions.
Types of Area of Influence
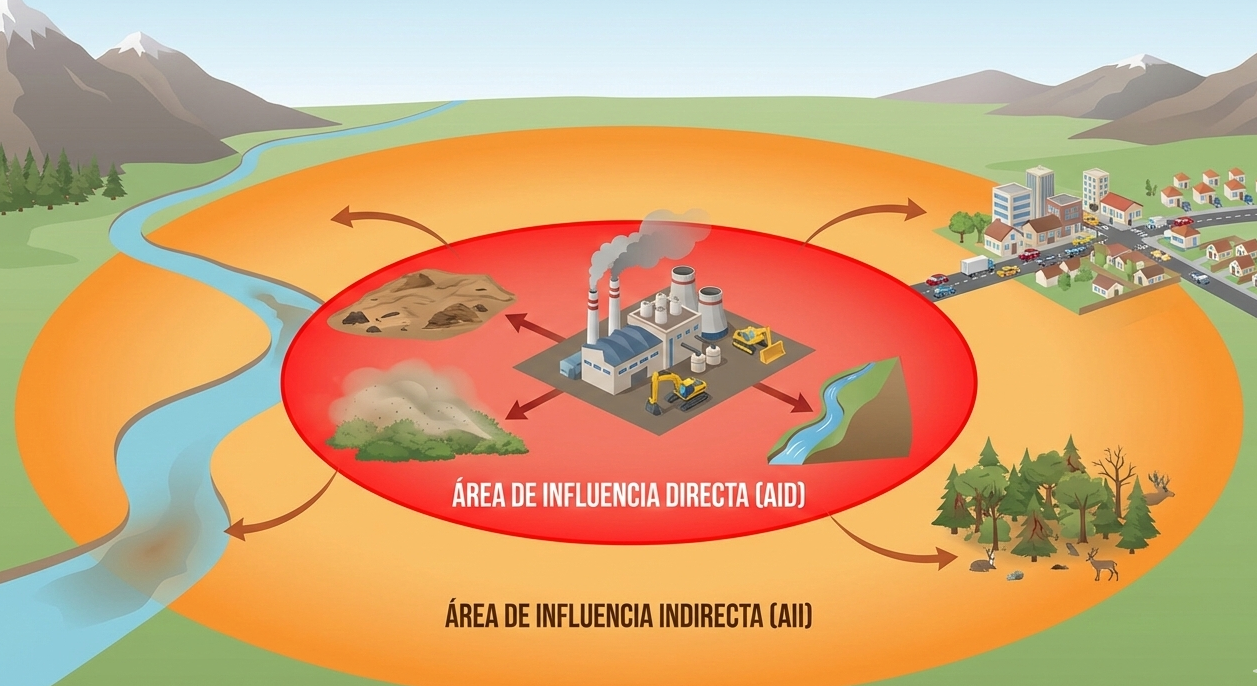
Direct Area of Influence
The Direct Area of Influence includes zones where project impacts occur immediately and as a direct consequence of project activities. These impacts typically affect land use, vegetation, wildlife, water resources, air quality, or nearby human activities.
This area represents the most evident cause–effect relationship between the project and the environment.
Indirect Area of Influence
The Indirect Area of Influence covers areas where impacts arise as secondary or induced effects, often over time or through interconnected environmental and social processes. These may include changes in resource use, population dynamics, or ecological connectivity.
Considering indirect influence is essential for a comprehensive and preventive environmental assessment.
How to Determine the Area of Influence?
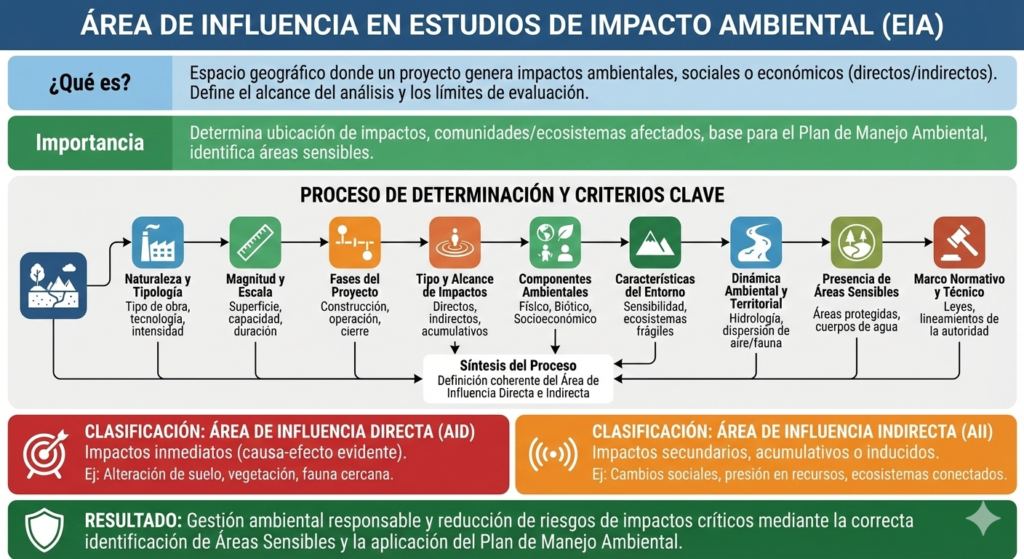
Determining the Area of Influence requires a structured and technically justified approach that defines how far project-related impacts may extend across environmental and social systems.
While methodologies may vary depending on project type and regulatory context, the process generally follows these steps:
1.Define the Project and Its Activities
The process begins with a detailed description of the project, including:
- Type and purpose of the activity
- Exact location
- Land occupation and associated infrastructure
- Operational processes
A clear project definition allows for accurate identification of potential impact sources.
2. Analyze Project Phases
Each project phase can generate different impacts:
- Construction
- Operation
- Maintenance
- Closure or decommissioning
The Area of Influence may change depending on the phase, particularly between construction and operation.
3. Identify Potential Environmental Impacts
Potential impacts are identified considering:
- Direct impacts
- Indirect impacts
- Cumulative impacts
- Synergistic impacts
The spatial extent of these impacts is the primary factor in defining the Area of Influence.
4. Assess Environmental Components Separately
The Area of Influence is determined independently for:
- Physical components (e.g., watersheds, air dispersion zones)
- Biological components (e.g., habitats, species movement)
- Socio-economic components (e.g., communities, economic activities)
These component-based areas are later integrated into a final Area of Influence.
5. Delimit Direct and Indirect Areas of Influence
Based on the analyses, boundaries are established for:
- Direct Area of Influence, where immediate effects occur
- Indirect Area of Influence, where secondary or induced effects may appear
These areas are typically represented through thematic maps to support technical validation.
6. Identify Sensitive Areas
Sensitive areas within or near the Area of Influence such as protected ecosystems, water bodies, or vulnerable communities are identified, as they may require adjustments to the initial boundaries.
7. Provide Technical and Regulatory Justification
Finally, the defined Area of Influence must be supported by:
- Clear methodological explanations
- Technical criteria
- Alignment with applicable environmental regulations
This justification is essential for regulatory approval and environmental decision making.
Area of Influence by Environmental Component

To achieve a more accurate and comprehensive assessment, the Area of Influence is commonly defined separately for each environmental component. This component-based approach allows environmental impacts to be identified and evaluated according to the specific dynamics of natural and social systems.
- Physical Component:
- Watersheds and surface or groundwater systems
- Air circulation patterns and pollutant dispersion
- Noise propagation
- Terrain stability and geomorphology
- These variables help determine how physical processes may transmit impacts beyond the immediate project area.
- Biological Component:
- Species distribution and mobility
- Ecological corridors and habitat connectivity
- Sensitive or protected ecosystems
- Areas of high biodiversity value
- Socio-Economic Component:
- Nearby communities and settlements
- Livelihoods and economic activities
- Access to services and infrastructure
- Social dynamics and cultural assets
Relationship Between the Area of Influence and Sensitive Areas
Within the Area of Influence, it is often possible to identify sensitive areas, understood as zones that require special attention due to their environmental, ecological, or social value.
Sensitive areas may include protected natural areas, water bodies, fragile ecosystems, or vulnerable communities. Their presence directly influences the design and implementation of prevention, mitigation, and compensation measures within an Environmental Impact Assessment.
The proper identification of sensitive areas strengthens responsible environmental management and significantly reduces the risk of severe or irreversible impacts.
Conclusions
The Area of Influence is a structural element of Environmental Impact Assessments, as it defines the spatial framework within which project impacts are analyzed. Proper determination and classification of the Area of Influence enhance the technical quality of the EIA, support informed environmental decision making, and contribute to more sustainable and responsible project planning.