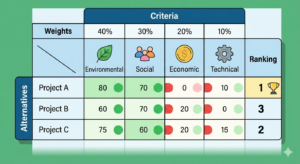
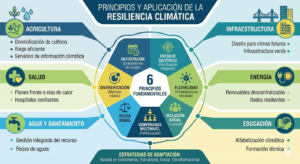
Climate mitigation refers to the actions, strategies, and policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions or enhancing carbon sinks in order to slow down global warming and limit the long term impacts of climate change. Today, climate mitigation is one of the most critical pillars of global climate action, alongside climate adaptation.
What Is Climate Mitigation?
Climate mitigation focuses on addressing the root causes of climate change, primarily by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) in the atmosphere.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), climate mitigation involves two core approaches:
- Reducing emission sources, especially from fossil fuels, industry, transport, and agriculture
- Increasing carbon sinks, both natural (forests, soils, oceans) and artificial (carbon capture technologies)
Unlike climate adaptation, which focuses on adjusting to the impacts of climate change, global warming mitigation aims to prevent those impacts from becoming more severe in the first place.
👉 Suggested : Climate Adaptation Explained
Why Climate Mitigation Is Critically Important
Environmental Importance
Effective climate mitigation strategies help to:
- Limit the rise in global average temperatures
- Reduce the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events
- Protect ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural carbon sinks
- Avoid irreversible climate tipping points, such as glacier collapse or coral reef loss
Social Importance
From a human perspective, mitigating climate change:
- Improves air quality and public health
- Reduces climate induced migration and displacement
- Lowers the risk of conflicts over water, food, and land
Economic Importance
Investing in climate mitigation delivers long term economic benefits:
- Prevents costly climate related damage
- Creates green jobs in renewable energy and efficiency sectors
- Encourages technological innovation
- Reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels
How Climate Mitigation Is Applied at Different Levels
International Level
Global climate mitigation efforts are coordinated through frameworks such as:
- The Paris Agreement, which aims to limit warming to well below 2°C, ideally 1.5°C
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
- International climate finance and technology transfer
National Level
At the country level, mitigation includes:
- Climate and energy laws
- National decarbonization strategies
- Carbon taxes and emissions trading systems
- Regulation of high emission industries
Regional and Local Level
Cities and regions play a crucial role through:
- Sustainable public transport systems
- Energy efficient buildings
- Waste management and circular economy initiatives
- Climate smart urban planning
Individual and Community Level
Individuals can contribute by:
- Reducing energy consumption
- Choosing sustainable transport
- Adopting low carbon diets
- Supporting climate friendly policies and education
Most Effective Climate Mitigation Strategies
Energy Transition
Strategy: Replace fossil fuels with clean energy sources.
Key measures include:
- Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy
- Phasing out coal power
- Electrification of transport
- Energy storage technologies
Countries such as Germany, China, and Denmark lead global efforts in renewable energy deployment.
Energy Efficiency
Strategy: Use less energy to achieve the same output.
Key measures include:
- Energy efficient buildings
- Low consumption appliances
- LED lighting
- Industrial efficiency standards
Energy efficiency remains one of the most cost effective climate mitigation strategies.
Sustainable Transport
Strategy: Reduce emissions from mobility.
Key measures include:
- Electric vehicles
- High quality public transport
- Cycling and walking infrastructure
- Alternative fuels such as hydrogen and biofuels
Nature Based Solutions
Strategy: Use ecosystems as carbon sinks.
Key measures include:
- Reforestation and afforestation
- Protecting forests and mangroves
- Regenerative agriculture
- Wetland restoration
⚠️ These solutions complement, but do not replace, emission reductions.
Agriculture and Food Systems
Strategy: Cut emissions from food production.
Key measures include:
- Sustainable farming practices
- Reduced food waste
- Low carbon diets
- Improved fertilizer management
Economic and Financial Instruments
Strategy: Use market incentives to drive emission reductions.
Key measures include:
- Carbon taxes
- Emissions trading systems (ETS)
- Clean energy subsidies
- Removal of fossil fuel subsidies
Technological Innovation
Strategy: Develop new mitigation technologies.
Key measures include:
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS)
- Green hydrogen
- Negative emission technologies
- Digital optimization of energy systems
Global Leaders in Climate Mitigation
| Country / Region | Key Actions |
|---|---|
| European Union | Climate neutrality by 2050 |
| Sweden | Carbon tax since the 1990s |
| Costa Rica | Nearly 100% renewable electricity |
| China | Largest investor in renewable energy |
| Japan | Hydrogen based energy strategies |
Key Challenges and Barriers to Climate Mitigation
Despite progress, major challenges remain:
- Dependence on fossil fuels
- Political and economic resistance
- Insufficient financing in developing countries
- Climate inequality
- Social opposition to rapid transitions
- Inadequate current commitments
Future Outlook for Climate Mitigation
Looking ahead, climate mitigation will be shaped by:
- Faster energy transitions
- Increased social and legal pressure
- Growth in green employment
- Integration of mitigation and adaptation
- Breakthrough innovations
- Stronger international cooperation
Frequently Asked Questions
What is climate mitigation in simple terms?
It means reducing the causes of climate change by cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
What are the most effective climate mitigation strategies?
Renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable transport, and nature based solutions.
Can individuals help mitigate climate change?
Yes, through energy savings, sustainable choices, and civic engagement.