What Is an Environmental Checklist and Why It Matters
An environmental checklist is a structured tool used to systematically evaluate environmental impacts, compliance, and management practices. Whether you’re screening a community project, auditing a manufacturing site, or monitoring field conditions, these checklists provide a consistent, reliable framework. They help identify potential risks early ensuring mitigation measures are in place and regulatory compliance is achieved and streamline decision-making throughout a project’s lifecycle.
Types of Environmental Checklists and Their Use Cases
- Environmental Screening Checklists: Common in development or funding contexts (e.g. Caribbean Development Bank projects), they are used during early project phases to flag possible environmental impacts and guide further assessment.
- Environmental Compliance Checklists: Widely used in manufacturing and industry—for example via platforms like Manifestly—these focus on regulatory obligations such as emissions, hazardous waste, equipment maintenance, PPE, and audit protocols.
- Environmental Monitoring Checklists: Often used in field inspections or site supervision to regularly check air and water quality, energy use, waste handling, and environmental management systems compliance.
Essential Elements of Every Environmental Checklist
Every effective checklist—whether screening, compliance, or monitoring should include:
- A clear purpose and scope, defining project type or operational context;
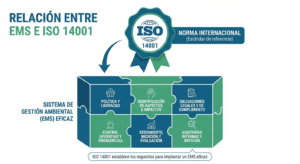
- Reference to legal and regulatory requirements, ensuring alignment with local, national, or international standards (ISO 14001) ;
- Sections on environmental aspects like emissions, waste, resource use, water discharge, biodiversity, and site hazards ;
- Items on mitigation, corrective action, monitoring, record‑keeping, and supervisory oversight.
- A consistent format with status indicators (e.g. Completed / Needs Attention / Not Applicable), timestamps, signature lines, and reviewer notes.
Step‑by‑Step: Designing an Effective Checklist
- 1. Identify Applicable Regulations and Standards: Reference local and international laws or certifications your organization must meet.
- 2. Define the Scope and Type: Choose between screening, compliance, or monitoring checklists, and define which operations they cover.
- 3. Structure by Categories: Organize by themes: emissions, energy, water, waste, noise, chemicals, etc.
- 4. Write Specific and Verifiable Items: Use actionable prompts like “Are spill kits in place?” or “Is wastewater pH within range?”
- 5. Add Instructions and References: Brief explanations, legal references, or SOP links improve clarity.
- 6. Include Completion Tools: Status markers, signature fields, notes, and timestamps are vital for documentation.
- 7. Choose the Right Format: Paper, spreadsheets, or platforms like Manifestly/Checklist.gg—each has its use case.
- 8. Pilot Test Before Rollout: Test in real-world settings. Gather feedback. Improve.
- 9. Train All Users: Run walkthroughs and offer support materials to standardize use.
- 10. Audit and Update Regularly: Review quarterly or annually. Adapt based on performance and evolving regulations.
Reference local and international laws or certifications your organization must meet.
Practical Examples: Industry, Construction, and Community
- Manufacturing: Emissions logs, waste handling, PPE checks, and equipment maintenance.
- Construction: Risk screening, soil erosion control, material management.
- Community Projects: Field inspections for water quality, vegetation protection, or recycling programs.
Digital Tools to Create and Manage Your Checklists
Platforms like Manifestly and Checklist.gg help digitize checklists, assign responsibilities, send reminders, store audit histories, and generate reports.
Benefits of Using Environmental Checklists Daily
- Ensures compliance and accountability
- Minimizes errors and oversight
- Enhances sustainability outcomes
- Reduces costs and penalties
- Boosts transparency and stakeholder trust
Legal Compliance: Why Environmental Checklists Are Essential
Environmental checklists ensure:
- Adherence to ISO 14001 and EPA regulations
- Real-time corrective actions
- Complete documentation during audits
- Lower risk of fines or shutdowns
Common Pitfalls When Implementing Checklists
- Generic content not tailored to the context
- Outdated checklists that don’t reflect new laws
- Poor training and inconsistent use
- Manual tracking instead of digital automation
How to Start Using Environmental Checklists Today
- Choose your checklist type
- Customize and structure logically
- Train your team
- Use digital tools
- Review and improve regularly
Checklists aren’t just forms—they’re proactive tools for reducing risk, improving sustainability, and ensuring environmental protection becomes part of everyday operations.