What Is an Environmental Management System?
An environmental management system (EMS) is a structured framework that helps organizations identify, manage, monitor, and improve their environmental performance. It provides a systematic approach to controlling environmental impacts, ensuring regulatory compliance, and supporting long term sustainability goals.
Unlike isolated environmental initiatives, an environmental management system integrates environmental considerations into daily operations, decision making, and strategic planning. For this reason, EMS frameworks are widely adopted across manufacturing, construction, energy, logistics, healthcare, and service industries.
At its core, an EMS enables organizations to move from reactive compliance to proactive environmental management.
How an Environmental Management System Works
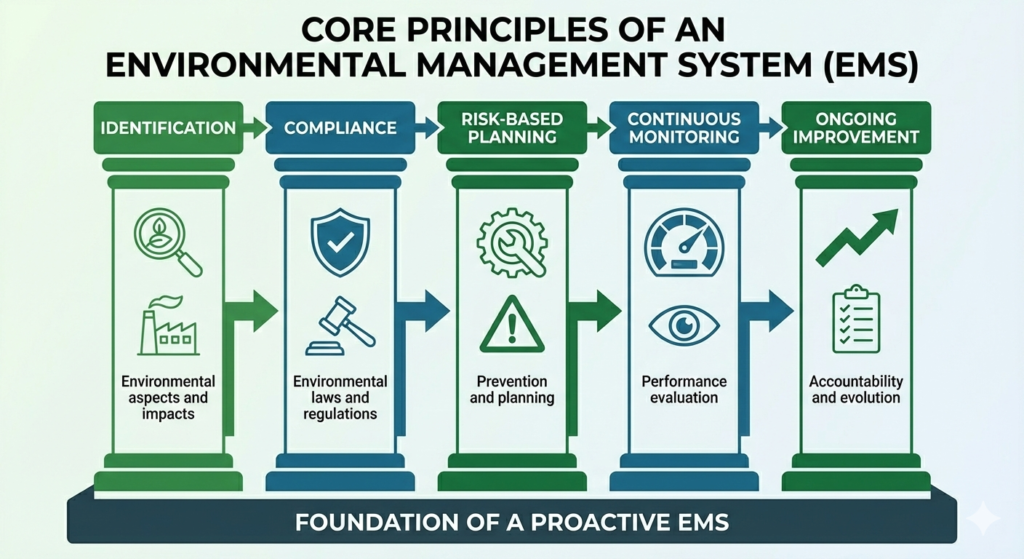
Core Principles of an EMS
An effective environmental management system is built on several fundamental principles:
- Identification of environmental aspects and impacts
- Compliance with environmental laws and regulations
- Risk based planning and prevention
- Continuous monitoring and performance evaluation
- Ongoing improvement and accountability
These principles ensure that environmental management becomes a repeatable, measurable, and auditable process rather than a one time effort.
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle Explained
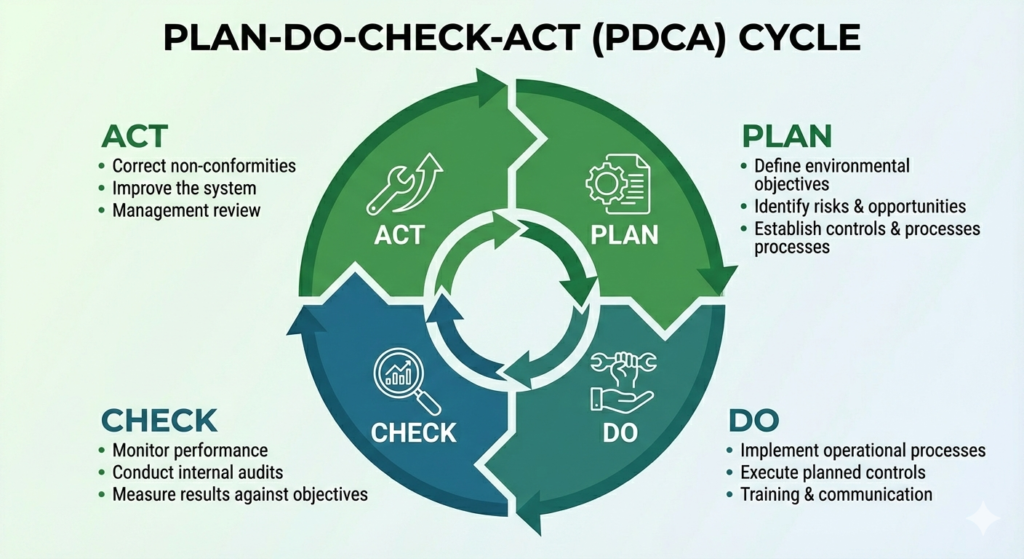
Most environmental management systems follow the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle:
- Plan: Define environmental objectives, identify risks, and establish controls
- Do: Implement operational processes and controls
- Check: Monitor performance, conduct audits, and measure results
- Act: Correct non conformities and improve the system
The PDCA cycle is a central requirement of ISO 14001 and is what enables continuous improvement in environmental performance.
Continuous Improvement in Environmental Performance
Continuous improvement ensures that an environmental management system evolves with changing regulations, operational risks, and stakeholder expectations. Organizations that actively use performance indicators, internal audits, and management reviews consistently achieve better environmental and business outcomes.
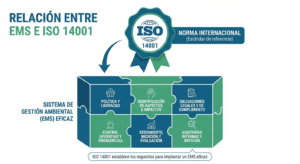
Environmental Management System and ISO 14001
What Is ISO 14001 and Why It Matters
ISO 14001 is the internationally recognized standard for environmental management systems. It defines the requirements an organization must meet to establish, implement, maintain, and improve an EMS.
ISO 14001 is part of the ISO 14000 family of standards and is applicable to organizations of any size, industry, or location. Its global recognition makes it a key trust signal for regulators, customers, investors, and supply chain partners.
ISO 14001 Requirements for an EMS
To comply with ISO 14001, an environmental management system must address:
- Environmental policy and leadership commitment
- Environmental aspects, impacts, and risks
- Legal and regulatory obligations
- Operational controls and emergency preparedness
- Monitoring, measurement, and evaluation
- Internal audits and management review
These requirements ensure that the EMS is not only documented but also effectively implemented and maintained.
ISO 14001 Accreditation vs Certification
The terms ISO 14001 accreditation and ISO 14001 certification are often confused.
- Certification refers to the organization being audited and certified against ISO 14001.
- Accreditation refers to the formal recognition of certification bodies by an accreditation authority.
Understanding this distinction is essential when selecting certification partners and preparing for audits.
Steps to Implement an Environmental Management System
- Defining Environmental Policy and Objectives
Implementation begins with a clear environmental policy aligned with the organization’s strategic direction. Objectives should be measurable, realistic, and linked to significant environmental aspects. - Identifying Environmental Aspects and Impacts
Organizations must systematically identify how their activities, products, and services interact with the environment. This includes emissions, waste, energy use, water consumption, and resource efficiency. - Operational Controls, Monitoring, and Audits
Operational controls ensure consistent performance, while monitoring and measurement provide data to assess effectiveness. Internal audits verify compliance and readiness for external ISO 14001 audits.
Environmental Management System vs EHS Management System
Key Differences Between EMS and EHS
An environmental management system focuses exclusively on environmental impacts and compliance.
An EHS management system integrates environmental, health, and safety requirements into a single framework.
While EMS is narrower in scope, EHS systems are often preferred in high-risk industries where worker safety and environmental protection are closely linked.
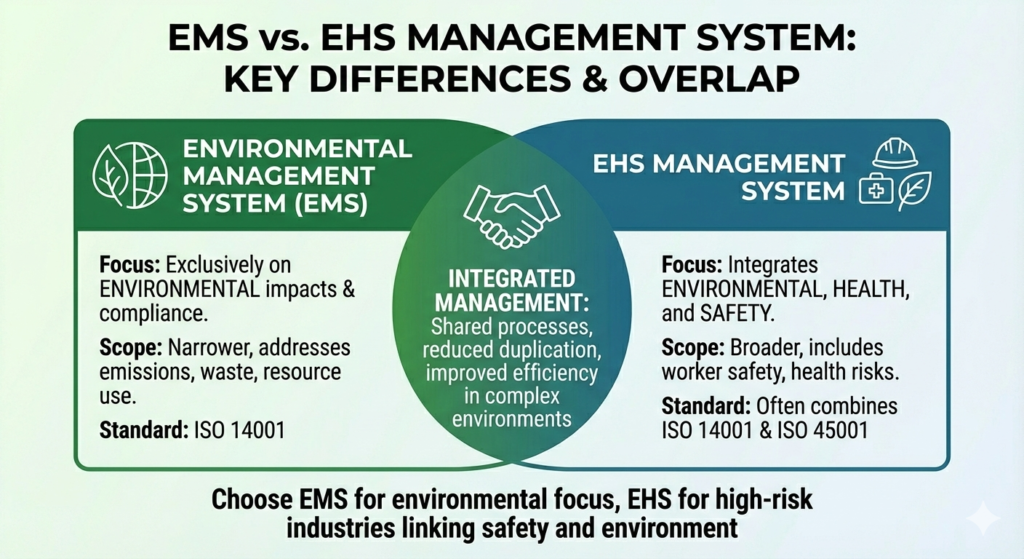
When to Use an Integrated Management System
Organizations operating in regulated or complex environments often benefit from integrating EMS with quality (ISO 9001) and occupational health and safety (ISO 45001) systems to reduce duplication and improve efficiency.
Benefits of an Environmental Management System
- Regulatory Compliance and Risk Reduction
An effective EMS helps organizations stay ahead of environmental regulations, reduce non compliance risks, and respond more effectively to inspections and enforcement actions. - Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
Environmental management systems often lead to reduced waste, lower energy consumption, and more efficient use of resources, directly improving cost control. - Reputation, Stakeholder Trust, and Sustainability Goals
ISO 14001-aligned EMS frameworks enhance corporate reputation, support ESG strategies, and strengthen relationships with customers, investors, and regulators.
ISO 14001 Accreditation: What Organizations Need to Know
- What 14001 Accreditation Involves
ISO 14001 accreditation ensures that certification bodies operate competently and impartially. For organizations, choosing an accredited certification body increases credibility and international recognition. - Preparing for an ISO 14001 Audit
Preparation involves closing compliance gaps, training staff, performing internal audits, and ensuring documented processes reflect actual operations. - Maintaining and Improving Accreditation Over Time
ISO 14001 certification is not a one-time achievement. Ongoing surveillance audits and continuous improvement are required to maintain certification and demonstrate long-term commitment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Environmental Management Systems
Is ISO 14001 Mandatory?
No, ISO 14001 is voluntary. However, many organizations adopt it due to customer requirements, regulatory pressure, or competitive advantage.
Which Organizations Need an EMS?
Any organization with environmental impacts can benefit from an EMS, regardless of size or sector.
How Long Does ISO 14001 Accreditation Take?
Implementation timelines vary, but most organizations take between three and twelve months, depending on complexity and readiness.
Conclusion
An environmental management system is a powerful tool for organizations seeking structured environmental control, regulatory compliance, and sustainable growth. When aligned with ISO 14001 accreditation, an EMS delivers measurable business value while strengthening environmental responsibility and stakeholder confidence.